Near-infrared fluorescence imaging is a technology that uses near-infrared light to excite and emit fluorescence signals to achieve imaging. Through this technology, we can observe fine structures and biomolecule information that cannot be seen in the while light mode. Let’s take a closer look at the principles and applications of near-infrared fluorescence imaging!
1.Principle of ICG Endoscopy System
Endoscopic surgery lacks tactile sensation and relies heavily on visual effects to feedback different types of tissue structures. Through NIR fluorescence endoscopy, real-time imaging of tissues and vessels underneath can be achieved to improve the visibility under the endoscope during surgery .
- NIR light (700-1000 nm) can penetrate deeply into tissues and has little interference from tissue autofluorescence.
- NIR fluorescent contrast agents maximize signal-to-background ratio and enhance contrast in different tissue types.
- Fluorescence signals are merged with normal RGB color video, allowing direct anatomical localization intraoperatively.

2.the mechanism of ICG staining

3.Schematic diagram of ICG organ and tissue imaging process
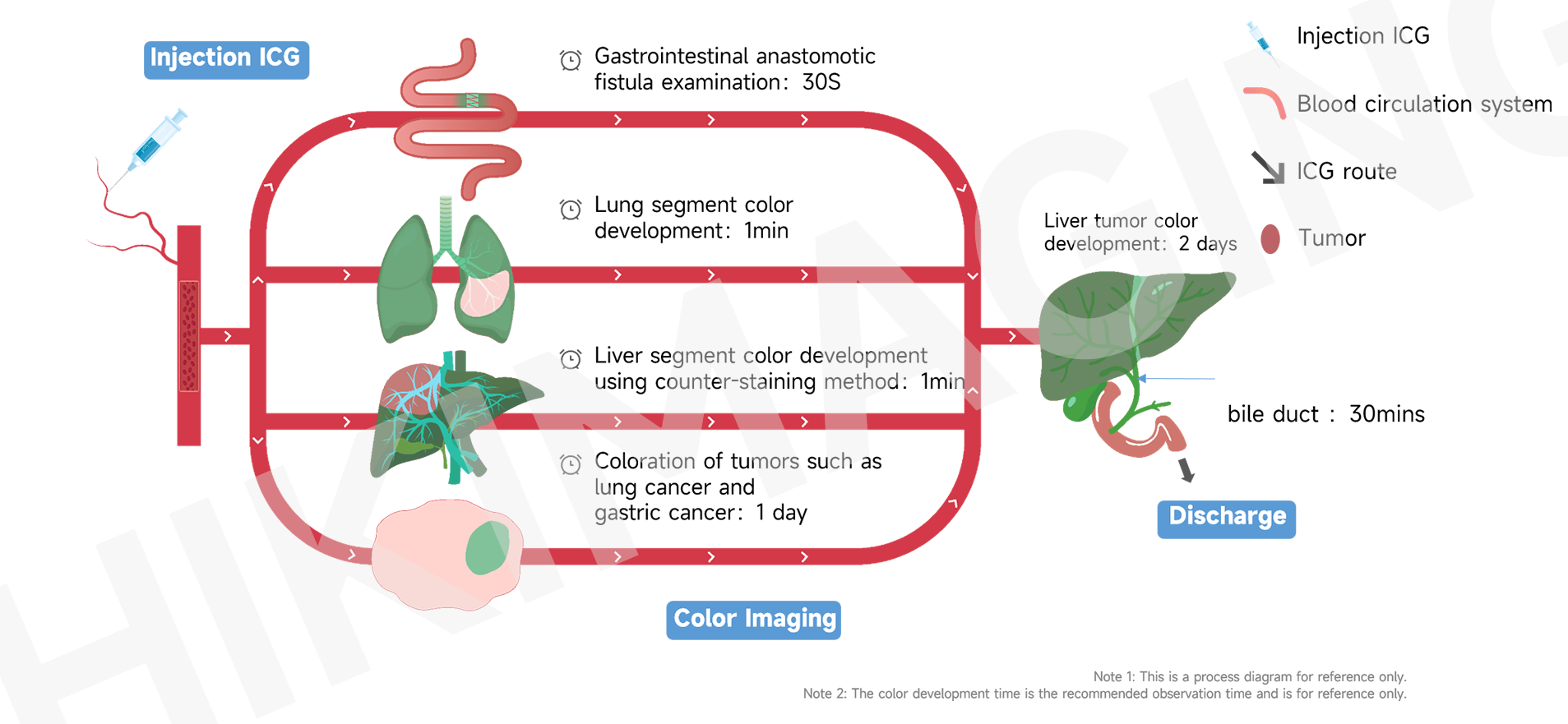
4.Schematic diagram of ICG sentinel lymph node imaging process
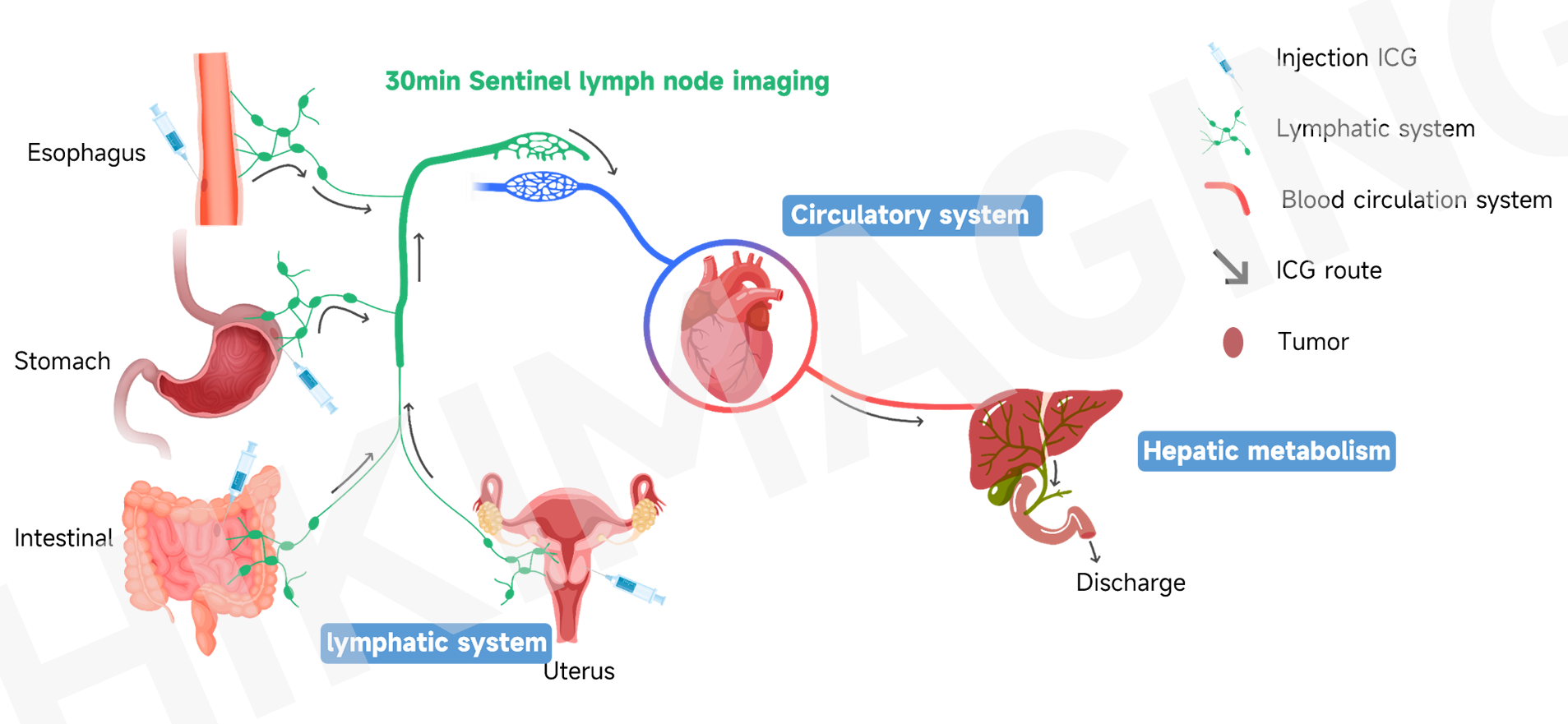
Thanks for watching.
 CN
CN
